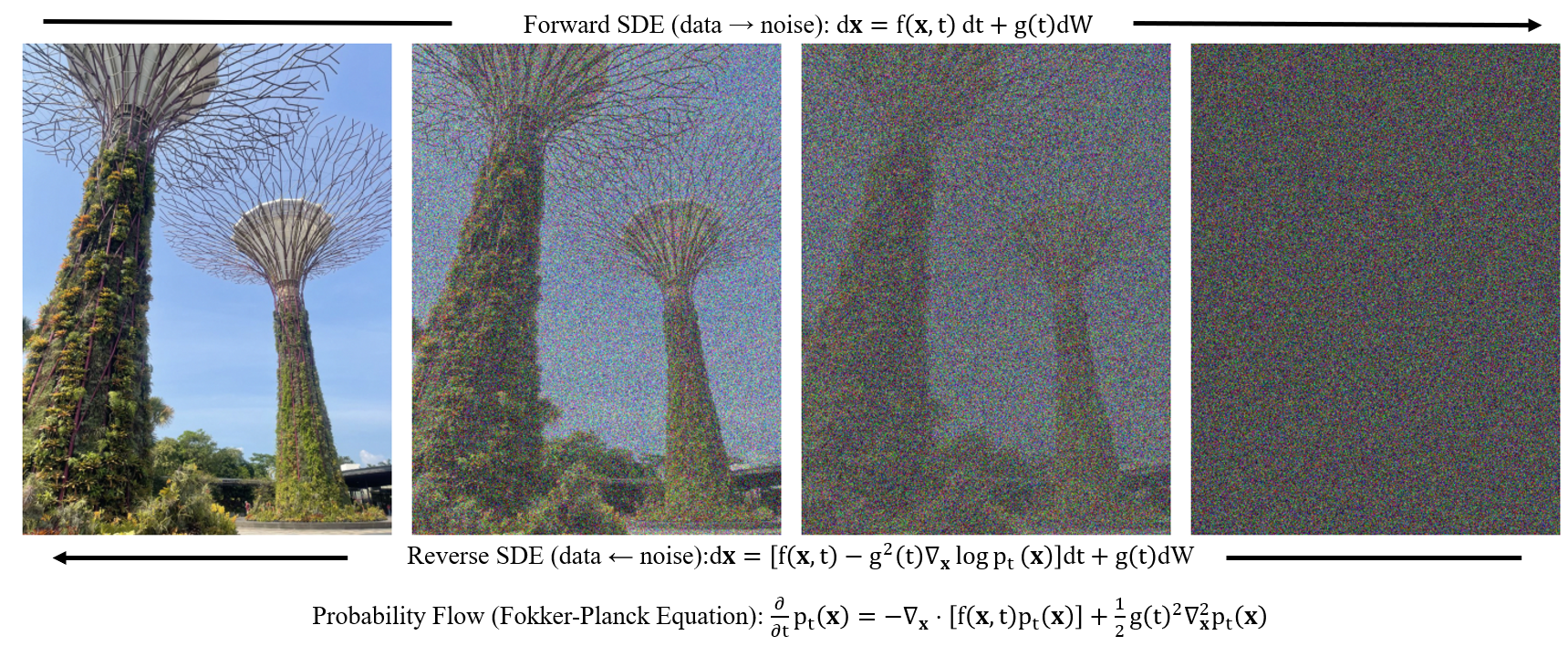
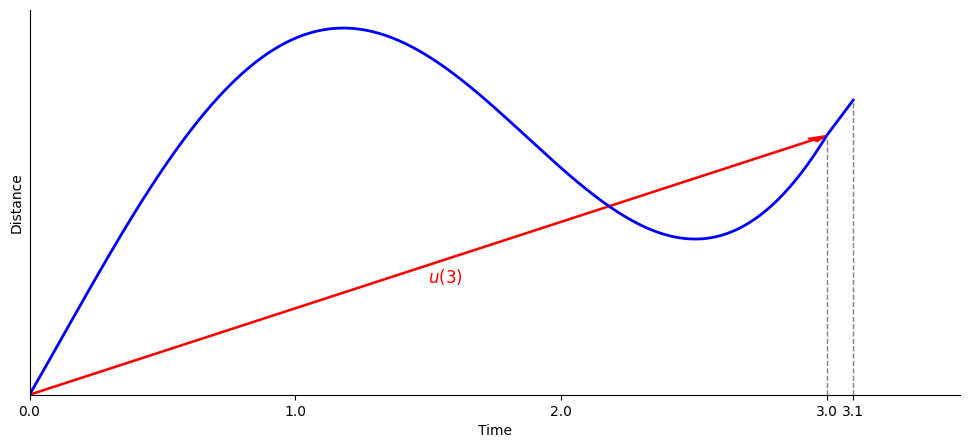
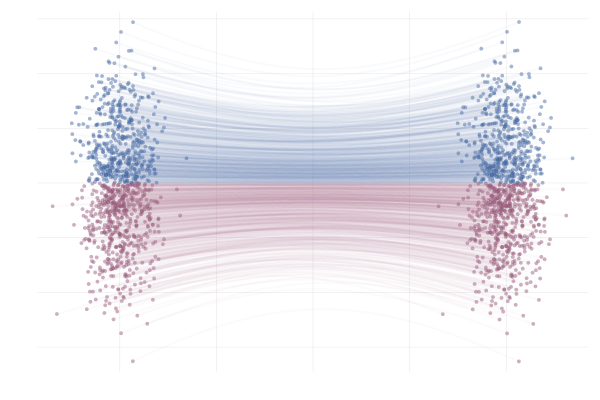
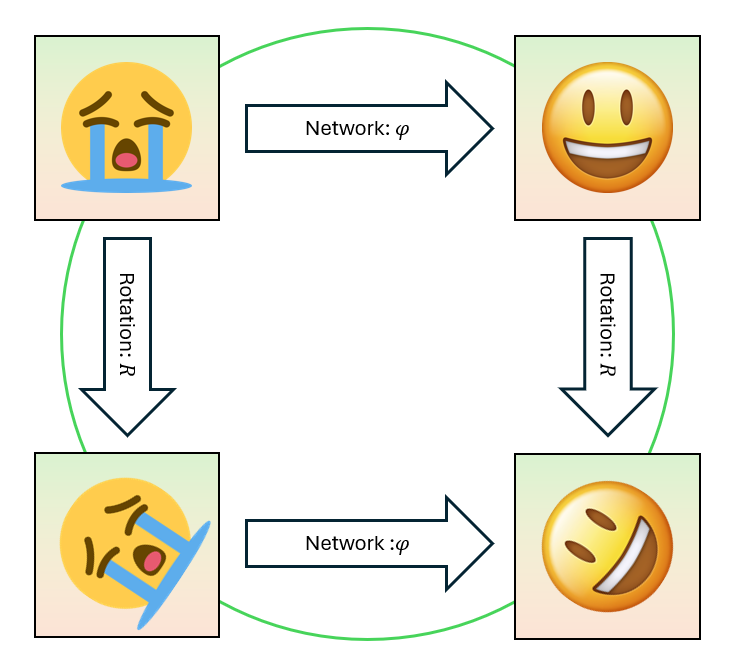
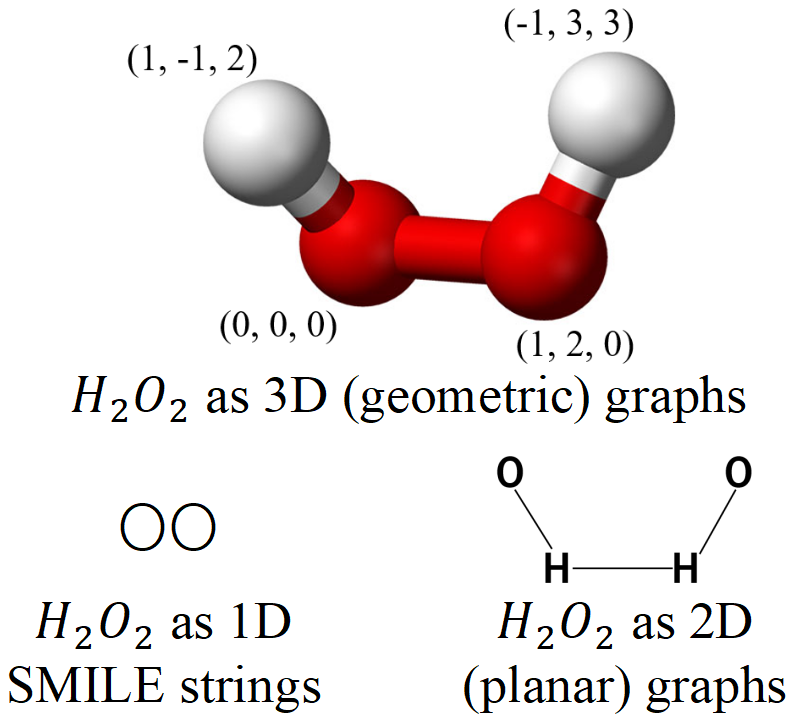
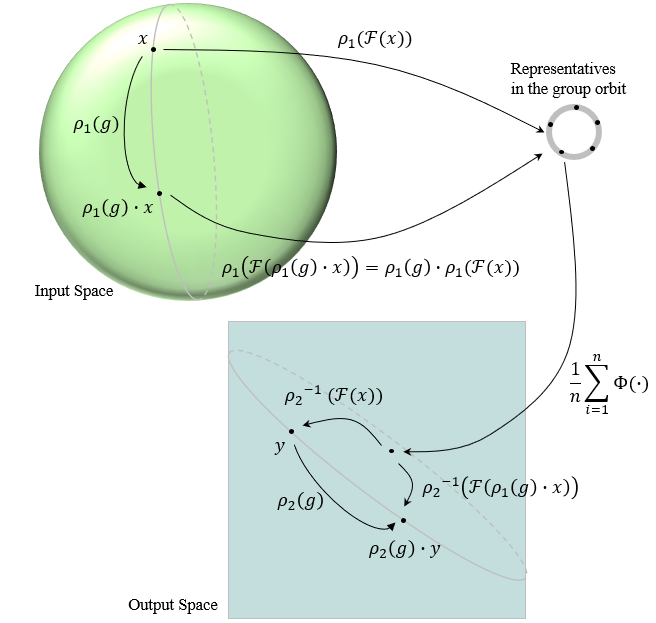
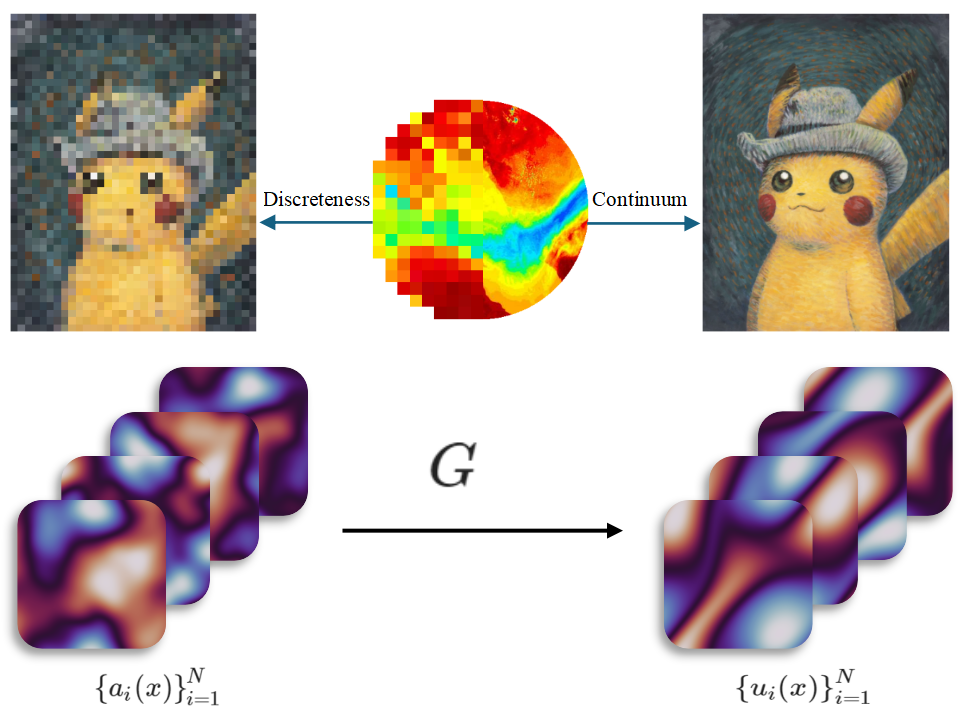
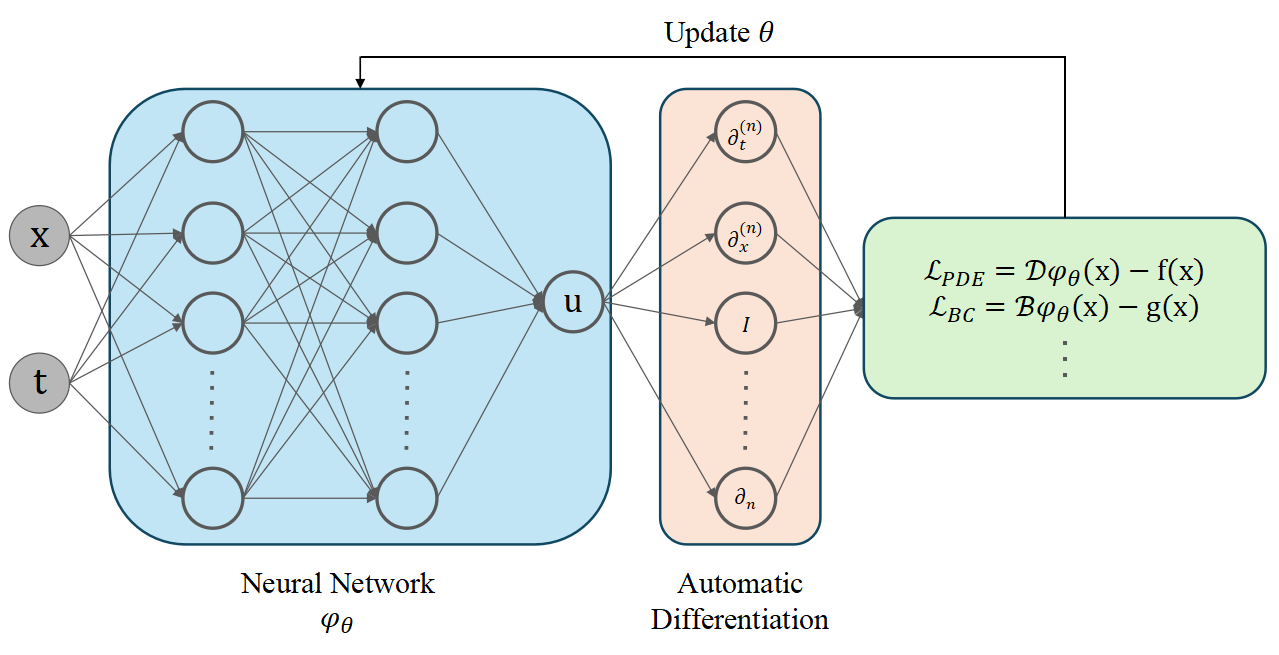
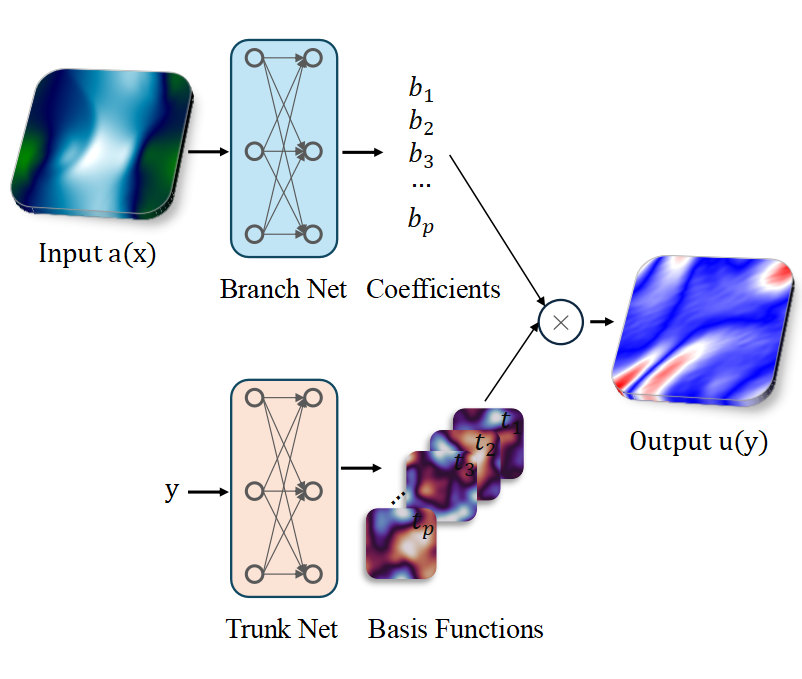
Much of the shared content (published papers, oral presentations, etc.) leans toward low-entropy, story-heavy narratives. My blogs aim to simplify fundamental concepts and underlying mechanisms. Minimal functioning code, but enough to grasp the underlying ideas, are provided in some blogs.
Technical BLOGs
- All
- Generative Models
- Equivariance
- Neural PDE Solvers
- Others
Contact
If you find any mistakes or have any suggestions, please email:
wenhan.gao![]() stonybrook.edu
stonybrook.edu